Explain the Concept of Probability With Different Approaches
The long-term proportion of times an event occurs during a random process. Hence The Probability of occurrence of Head on tossing a coin is.
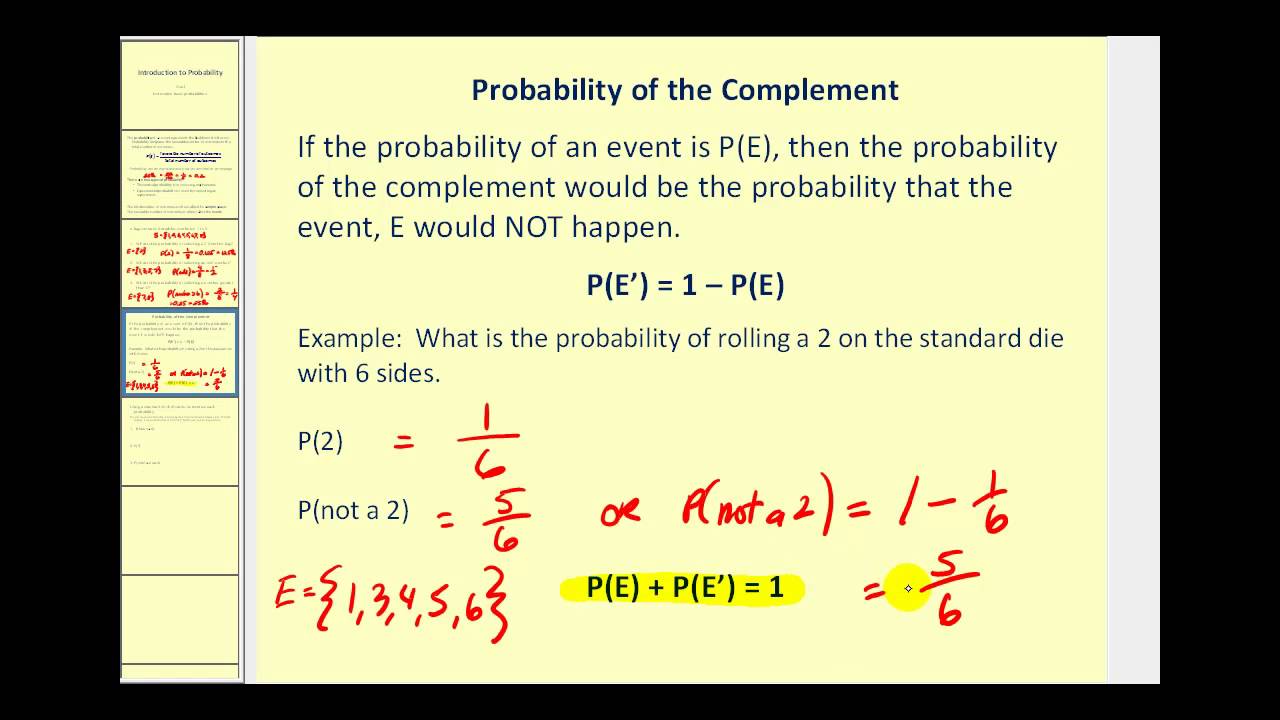
The Terminology Of Probability Introduction To Statistics
Probability can range in from 0 to 1 where 0 means the event to be an impossible one and 1 indicates a certain event.

. It can either be marginal joint or conditional. You can think of probabilities as being the following. If there are moutcomes in a sample space universal set and all are equally likely of being the result of an experimental measurement then the probability of observing an event a subset that contains soutcomes is given by.
The Concept of Probability Probability theory is the rational way to think about uncertainty. Explain the concept of probability theory. It is mainly based on the data that is obtained after an experiment is carried out.
The closer the probability is to zero the less likely it is to happen and the closer the. The classical definition of probability classical probability concept states. If an event has a probability of zero that tells you the event is impossible and wont happen.
Experimental Probability for an Event A can be calculated as follows. There are four strategies you can use to increase the probability of success in business. The outcome of a random event cannot be determined before it occurs but it may be any one of several possible outcomes.
For example if three coin tosses yielded a head the empirical probability of getting a head in a coin toss is 100. If an event has a probability of one that tells you the event is certain and will happen. There are eight possible outcomes.
Probability theory a branch of mathematics concerned with the analysis of random phenomena. Where you can buy latest ignou solution or post your assignment from contact page. Given the large number of different approaches it may not be a surprise that even today nearly 500 years after the concept of probability was first used there are competing ways of defining its exact meaning.
Experimental Probability Experimental probability is a probability that is calculated based on multiple experiments. Certain probability of 1 the highest possible likelihood likely probability between ½ and 1 even chance probability of ½. Experimental Probability is found by repeating the experiment and observing outcomes.
Probabilities can be expressed as proportions that range from 0 to 1 and they can also be expressed as percentages ranging from 0 to 100. We can predict only the chance of an event to occur ie. Classical probability is the statistical concept that measures the likelihood of something happening but.
Probability is a measure of the likelihood of an event to occur. Also explain what are the different approaches to probability theory. The value p 0 corresponds to the outcome e being impossible and the value p 1 corresponds to the outcome e being certain.
HHH HHT HTH HTT THH THT TTH TTT. Apart from subjective probabilities there are two other main types of probabilities. Many events cannot be predicted with total certainty.
Probability is a statistical concept that measures the likelihood of something happening. This approach traces back to the field where probability was first sistematically employed which is. It provides the probabilities of different possible occurrences.
Similarly The Probability of occurrence of Tail on tossing a coin is. These two definitions derive from two different approaches to the concept of probability. This approach was formally introduced in the field of natural.
Also read events in probability here. Probability theory analyzes the chances of events occurring. Thus probability of falling head is 50 or 12 and falling tail is also 50 or 12.
Once you know the probability you can determine the likelihood of an event which falls along this range. The definition of probability is the likelihood of an event happening. P E number of favorable outcomes total number of outcome Example.
Frequency-based or empirical approach. To recall the probability is. Empirical probability Empirical probability refers to a probability that is based on historical data.
The actual outcome is considered to be determined by chance. PT 12 Experimental Probability. Identify trends or patterns in outcomes.
The probability of the complementary event A of A is given by P A 1 P A. The events A and A are mutually disjoint and together they form the whole sample space. When we toss an unbiased coin it may fall head or tail.
The propensity for a particular outcome to occur. In Statistics the probability distribution gives the possibility of each outcome of a random experiment or event. If we toss two unbiased coins they may fall in a number of ways as HH two heads HT 1st coin head and 2nd coin tail TH 1st coin-tail and 2nd coin head or TT two tails.
If an event has a probability between zero and one that tells you how likely the event is to happen. A A S P A A P S or P A P A P S 1 P A 1 P A. This means the probability of an event P E of a sample size is equal to the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of that situations outcome.
Target a range of outcomes centered around what is most likely. The probability of an outcome e in a sample space S is a number p between 0 and 1 that measures the likelihood that e will occur on a single trial of the corresponding random experiment. In the real world there are many examples of multinomial probability distributions.
Using Probability to Increase the Odds of Success. It is the branch of mathematics devoted to measuring quantitatively the likelihood that a given event will occur. The probability of each outcome can be calculated using the Multinomial Probability Formula.
Dont rely solely on single outcomes. Mathematical probability is expressed in fractions ½ and percentages 50. How likely they are to happen using it.
2 are blue 5 are yellow and 3 are red. Visit for ignou assignment solved. Theoretical probability is the ratio of the number of favourable outcomes to the total outcomes.
Classical frequency-based and subjective approaches Classical approach. Perhaps the first thing to understand is that there are different types of probability. There are 10 pillows in a bed.
If A is an event then the marginal probability is the probability of that event occurring P A. A probability of 0 indicates that there is no chance that a particular event will occur whereas a probability of 1 indicates that an event is certain to occur. The word probability has several meanings in ordinary conversation.
These differences do have consequences with respect to some of the statistical analyses one performs but fortunately it is. For example consider flipping a coin three times.
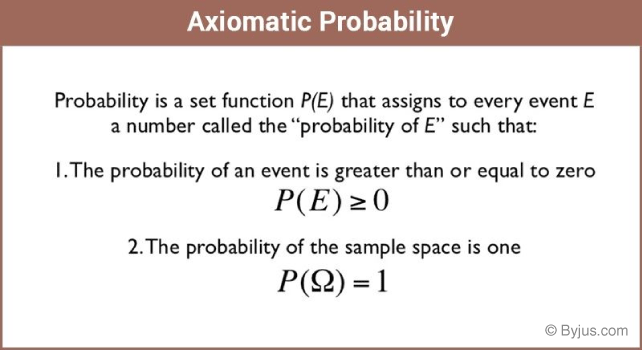
Axiomatic Probability Definition Conditions Examples

P Values Statistics Math Data Science Learning P Value

Probability Learning Through Technology Probability Teaching Strategies Learning

15 Concept Of Probability Classical And Frequency Approach To Any Problem Youtube Probability Data Science Concept
0 Response to "Explain the Concept of Probability With Different Approaches"
Post a Comment